追查问题,主要是在:
- 浮现问题
- 缩小范围
- 猜测,修正及验证
我们这里使用如下测试代码演示:
1 |
|
进程
我们通常可以使用top 命令查看到某一个进程占用了较高的CPU Loading。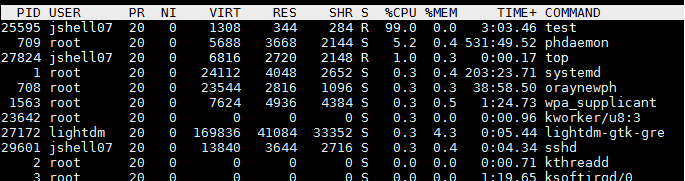
线程
可以通过top -H -p <pid> 命令具体查看<pid> 进程的子线程占用CPU Loading的情况。
这里是单独一个进程,是以这里只是单单出现一个。
函数
在定位到某一个线程之后,我们需要继续定位到某一个函数或者命令导致了CPU 占用过高。strace -p <pid> 命令能帮助查找到具体的函数。pstack <pid>, trace -p <tid>等命令也能给予我们一些启示。