1. Method with cryptographic
用户空间的方式有如下方式:
- netlink (AF_ALG) socket 的形式(kernel 已经merge进入主线)
- ioctl (OpenBSD 的形式, kenrel 没有merge此部分代码 )
- openssl
我们常见的userspace 与kernel space 之间通信的方式有:
- IOCTL
- /proc
- /sys
- netlink
我们主张使用socket 的方式,更为优雅与灵活。有人在此基础上封装了lib, libkcapi
2. netlink(socket)
2.1. data structure
<linux/if_alg.h>1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
struct sockaddr_alg {
__u16 salg_family;
__u8 salg_type[14];
__u32 salg_feat;
__u32 salg_mask;
__u8 salg_name[64];
};
struct af_alg_iv {
__u32 ivlen;
__u8 iv[0];
};
/* Socket options */
/* Operations */
Currently, the following ciphers are accessible:
- Message digest including keyed message digest (HMAC, CMAC)
- Symmetric ciphers
- AEAD ciphers
- Random Number Generators
我们可以使用如下的sockaddr_alg 的实例联系到具体的算法上。
1 | /* salg_type support: |
socket 中的family AF_ALG, setsockopt 使用 SOL_ALG。如果header 中没有申明,可以使用如下定义:1
2
3
4
5
6
2.2. Kernel internal
在kenrel 内部注册了AF_ALG family 类型的socket。在kernel/crypto/af_alg.c
1 | static struct proto alg_proto = { |
在kernel/crypto/algif_skcipher.c, 类似的algif_hash.c 注册了hash 类型的对象。1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23static struct proto_ops algif_skcipher_ops = {
.family = PF_ALG,
.release = af_alg_release,
.sendmsg = skcipher_sendmsg,
.sendpage = skcipher_sendpage,
.recvmsg = skcipher_recvmsg,
.poll = skcipher_poll,
};
static const struct af_alg_type algif_type_skcipher = {
.bind = skcipher_bind,
.release = skcipher_release,
.setkey = skcipher_setkey,
.accept = skcipher_accept_parent,
.ops = &algif_skcipher_ops,
.name = "skcipher",
};
static int __init algif_skcipher_init(void)
{
return af_alg_register_type(&algif_type_skcipher);
}
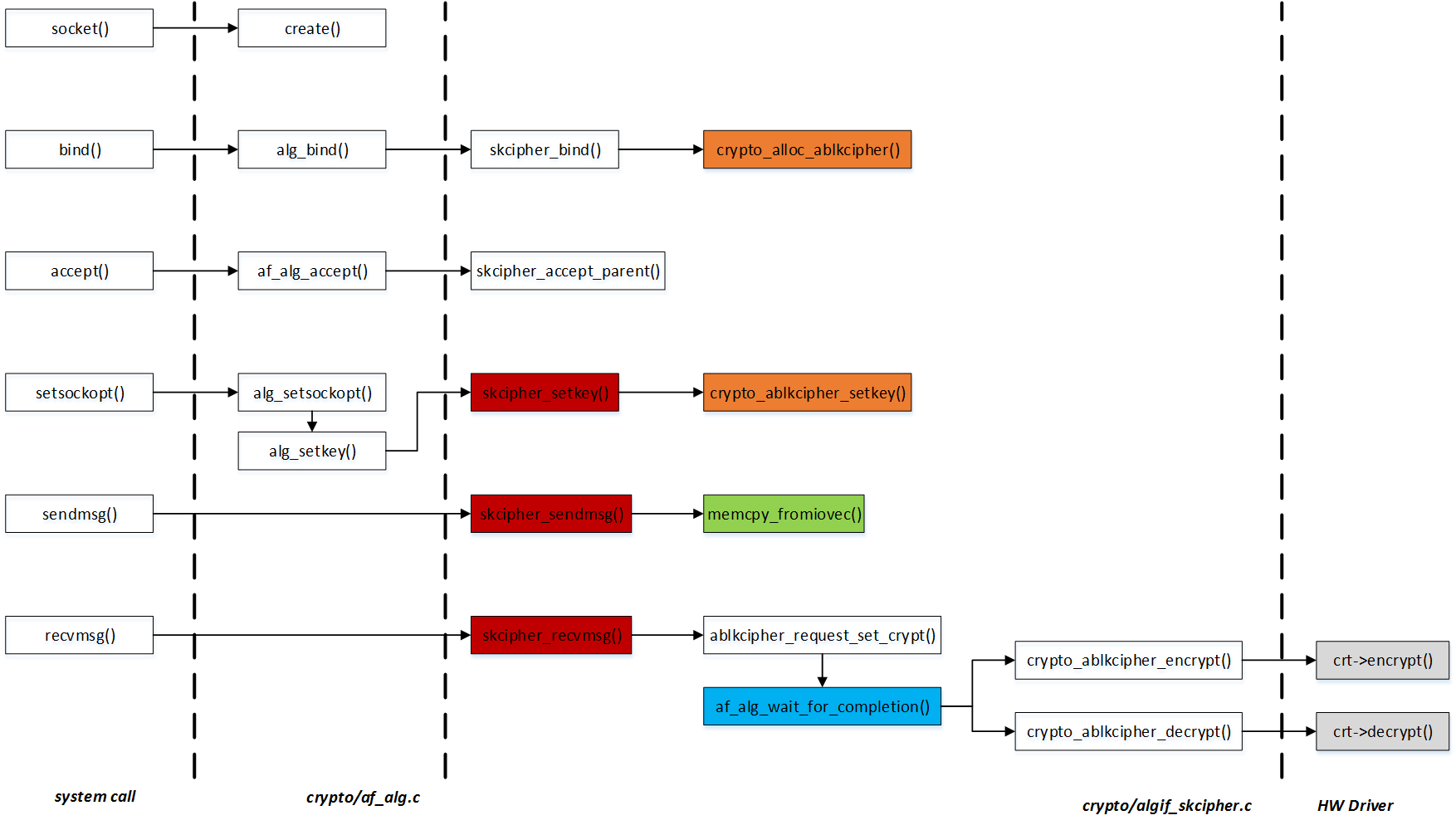
2.3. usage flow
我们使用如下流程进行使用:
- create socket with AF_ALG
- bind socket with sockaddr_alg addr.
- set key, setsocketopt()
- accept with socket. accept system call return new file descriptor.
- use new fd to sendmsg(), recvmsg()
Setsockopt Interface
我们可以是用setsockopt() 系统调用进行设定。
1 |
|
2.4. usage
1 |
|
3. openssl
3.1. afalg engine
我们再1.1.0 版本后的openssl/engines 可以找到e_afalg.c 模块。在1.1.1c 版本中支持的afalg 只有三种:
- aes_128_cbc
- aes_192_cbc
- aes_256_cbc
1 | static int afalg_ciphers(ENGINE *e, const EVP_CIPHER **cipher, |
openssl 内部的afalg engine 其实与自己写的userspace code 类似,都是使用netlink AF_ALG family socket。
1 | static ossl_inline void afalg_set_op_sk(struct cmsghdr *cmsg, |
openssl 中体现的优点在于:
- 使用EVP 抽象统一all engines, 比如afalg, crypdev 等
- 使用async io
- 支持zero copy (vmsplice(), splice() 函数使用)
3.2. performance
使用openssl speed 模块可以测试速度。
time openssl speed -evp aes-128-cbc -elapsed
time openssl speed -evp aes-128-cbc -elapsed -engine afalg
| Method | Result |
|---|---|
| Software Crypto | type 16 bytes 64 bytes 256 bytes 1024 bytes 8192 bytes 16384 bytes aes-128-cbc 13681.29k 16959.06k 18170.71k 18484.91k 18590.38k 18573.99k real 0m 18.67s user 0m 18.10s sys 0m 0.19s |
| Hardware Crypto | type 16 bytes 64 bytes 256 bytes 1024 bytes 8192 bytes 16384 bytes aes-128-cbc 293.11k 1052.46k 4073.64k 11785.59k 27314.86k 30938.45k real 0m 18.24s user 0m 0.73s sys 0m 10.80s |