在看openssl 1.1.1c 版本源码时,看到有一个zero copy 的字样。这里zero copy(零拷贝)主要指Kernel space 与user space 之间的拷贝过程。
1.Normal R/W
1 |
|
在read/write 时,需要将userspace 的数据copy 到kernel space。kerne 中用到的函数就有:
copy_from_user()
copy_to_user()
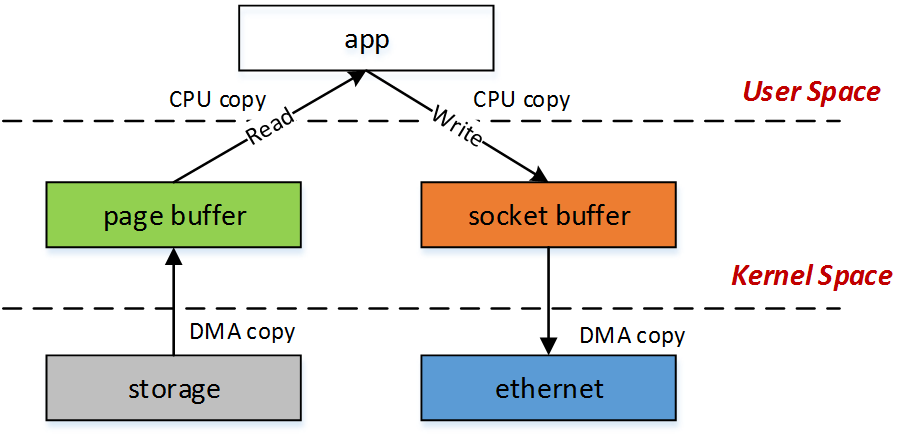
mmap() 能减少read 的copy 动作,直接映射kernel空间到用户空间,但是在write时, 还是需要将write_data_buffer 拷贝到kernel space.
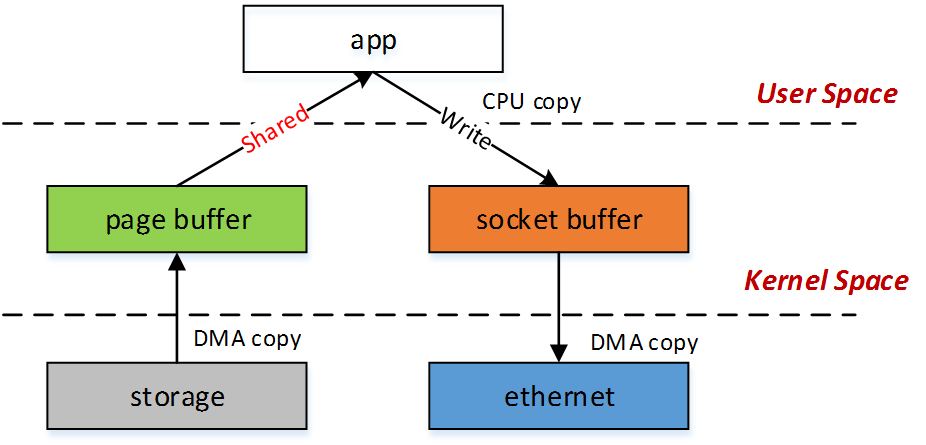
在拷贝文件时,我们可以这样减少copy 的次数。1
2
3
4size_t filesize = stat_buf.st_size;
source = mmap(0, filesize, PROT_READ, MAP_SHARED, f_in, 0);
target = mmap(0, filesize, PROT_WRITE, MAP_SHARED, f_out, 0);
memcpy(target, source, filesize);
2.zero copy
常见的zero copy 涉及到的函数有:
- sendfile
- vmsplice, splice
- tee
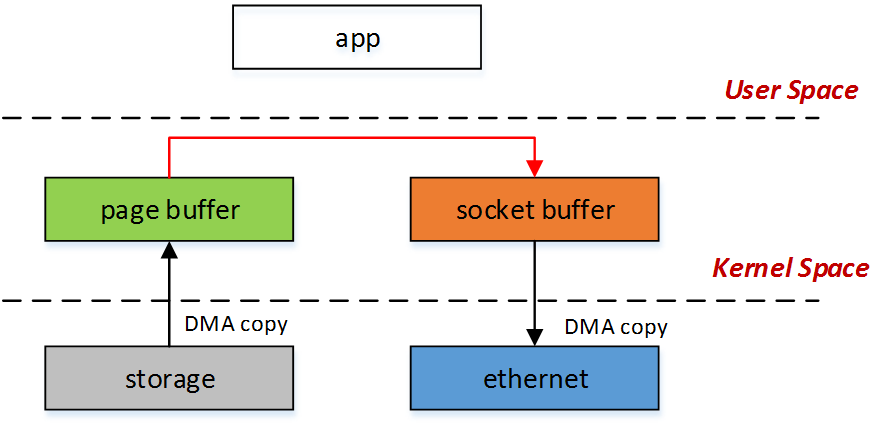
除vmsplice() 是映射函数外,其他借助管道实现,而管道有众所周知的空间限制问题,超过了限制就会hang住,所以每次写入管道的数据量好严格控制,保守的建议值是一个内存页大小,即PAGE_SIZE, 常见为4k。
splice用于在两个文件间移动数据,而无需内核态和用户态的内存拷贝,但需要借助管道(pipe)实现。大概原理就是通过pipe buffer实现一组内核内存页(pages of kernel memory)的引用计数指针(reference-counted pointers),数据拷贝过程中并不真正拷贝数据,而是创建一个新的指向内存页的指针。也就是说拷贝过程实质是指针的拷贝.
1 |
|
| system api | remarks |
|---|---|
| sendfile() | sendfile的in_fd必须指向支持mmap的文件,也就是真实存在的文件,而不能是socket、管道等文件 |
| splice() | splice()函数可以在两个文件描述符之间移动数据,且 其中一个描述符必须是管道描述符 |
| tee() | 仅支持在两个管道描述符之间复制数据 |
splice() 通过pipe 零拷贝文件的用例。
file_in -> pipe[1] (write end) -> pipe0 -> file_out
1 | int pipefd[2], off_in = 0, off_out = 0; |
参看资料
linux网络编程:splice函数和tee( )函数高效的零拷贝