1. Kernel Timer 软件架构
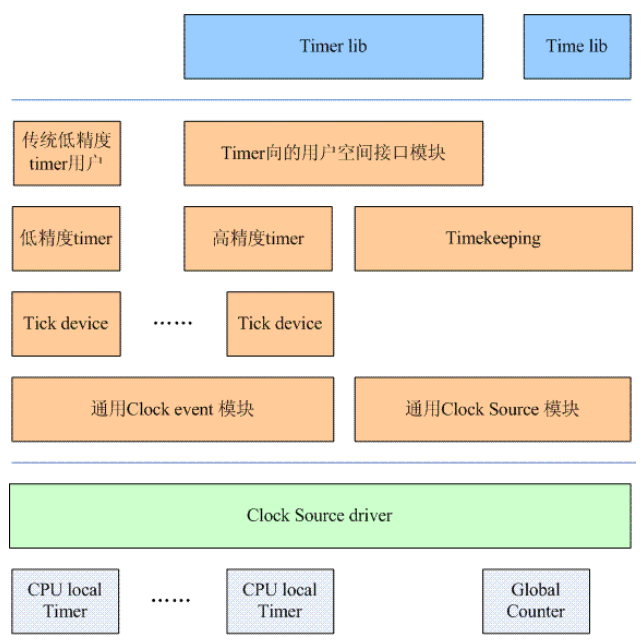
| 术语 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Global Counter | free running system counter, 可以参看arm_arm 手册里的Generic Timer->system counter。Rollover 时间至少40年。他提供了一个基础的timeline, 无线延伸 |
| CPU local Timer | CPU local timer 可以是Peripheral HW Timer, 或者是CPU 如ARM 含有的Generic Timer -> timer. |
| clock event | 通过timer硬件的 中断处理函数 完成的,在此基础上可以构建tick模块。clock event 是在timeline 上指定点产生event。 |
| tick 模块 | 维护了系统的tick,各个 进程的时间统计 也是基于tick的,内核的 调度器 根据这些信息进行调度。System Load和Kernel Profiling模块 也是基于tick的,用于计算系统负荷和进行内核性能剖析。 |
| timekeeping模块 | 系统时间, 每tick 的发生,其值增加。高进度的值,可以来源于clocksource |
| timer lib | 用户空间需求:1.获取系统时间,time, stime, gettimeofday, 2.定时器功能,settimer, alarm等 |
一个CPU 可以有多个local Clock Event, 但是会选择一个适合的作为tick device。
tick device 工作模式:
- one shot mode(提供高精度的clock event)
- periodic mode
一般有多少个cpu,就会有多少个tick device - local tick device, 在所有device 中会选取一个做global tick device, 负责维护整个系统的jiffies,更新wall clock,计算全局负荷等。
当系统处于高精度timer的时候(tick device处于one shot mode),系统会setup一个特别的高精度timer(可以称之sched timer),该高精度timer会周期性的触发,从而模拟的传统的periodic tick,从而推动了传统低精度timer的运转。因此,一些传统的内核模块仍然可以调用经典的低精度timer模块的接口。
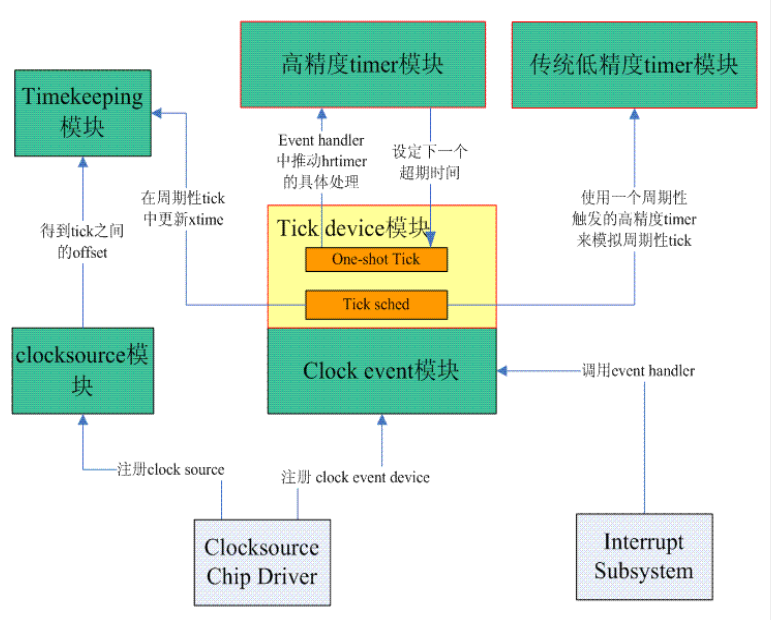
2. file structure
| 文件 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| time.c timeconv.c |
用户空间函数,time, stime, gettimeofday,alarm等,以及转换函数 |
| time_list.c time_status.c |
向用户空间提供的调试接口。在用户空间,可以通过/proc/timer_list接口可以获得内核中的时间子系统的相关信息。 |
| posix-timer.c posix-cpu-timers.c posix-clock.c |
POSIX timer, clock模块 |
| alrmtimer.c | alarmtimer 模块 |
| ntp.c | NTP 模块 |
| timerkeeping.c timerkeeping_debug.c |
timerkeeping.c模块 |
| ick-common.c tick-oneshot.c tick-sched.c |
tick device layer模块。 tick-common.c文件是periodic tick模块,用于管理周期性tick事件。 tick-oneshot.c文件是for高精度timer的,用于管理高精度tick时间。 tick-sched.c是用于dynamic tick的。 |
| tick-broadcast.c tick-broadcast-hrtimer.c |
broadcast tick模块。 |
| sched_clock.c | 通用sched clock模块。这个模块主要是提供一个sched_clock的接口函数,可以获取当前时间点到系统启动之间的纳秒值。底层的HW counter其实是千差万别的,有些平台可以提供64-bit的HW counter,我们可以不使用这个通用sched clock模块(不配置CONFIG_GENERIC_SCHED_CLOCK这个内核选项),而在自己的clock source chip driver中直接提供sched_clock接口。使用通用sched clock模块的好处是:该模块扩展了64-bit的counter,即使底层的HW counter比特数目不足(有些平台HW counter只有32个bit)。 |
| clocksource.c jiffies.c |
clocksource.c是通用clocksource driver。其实也可以把system tick也看成一个特定的clocksource,其代码在jiffies.c文件中 |
| clockevnet.c | clockevent 模块 |
| timer.c | 传统的低精度timer 模块, 基本tick |
| htimer.c | 高精度timer |
3. clocksource
时间其实可以抽象成一条直线, timeline. clock source就是用来抽象一个在指定输入频率的clock下工作的一个counter。输入频率可以确定以什么样的精度来划分timeline(假设输入counter的频率是1GHz,那么一个cycle就是1ns)
clocksource 数据结构如下:1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78/* linux-4.9.198 code */
/**
* struct clocksource - hardware abstraction for a free running counter
* Provides mostly state-free accessors to the underlying hardware.
* This is the structure used for system time.
*
* @name: ptr to clocksource name
* @list: list head for registration
* @rating: rating value for selection (higher is better)
* To avoid rating inflation the following
* list should give you a guide as to how
* to assign your clocksource a rating
* 1-99: Unfit for real use
* Only available for bootup and testing purposes.
* 100-199: Base level usability.
* Functional for real use, but not desired.
* 200-299: Good.
* A correct and usable clocksource.
* 300-399: Desired.
* A reasonably fast and accurate clocksource.
* 400-499: Perfect
* The ideal clocksource. A must-use where
* available.
* @read: returns a cycle value, passes clocksource as argument
* @enable: optional function to enable the clocksource
* @disable: optional function to disable the clocksource
* @mask: bitmask for two's complement
* subtraction of non 64 bit counters
* @mult: cycle to nanosecond multiplier
* @shift: cycle to nanosecond divisor (power of two)
* @max_idle_ns: max idle time permitted by the clocksource (nsecs)
* @maxadj: maximum adjustment value to mult (~11%)
* @max_cycles: maximum safe cycle value which won't overflow on multiplication
* @flags: flags describing special properties
* @archdata: arch-specific data
* @suspend: suspend function for the clocksource, if necessary
* @resume: resume function for the clocksource, if necessary
* @owner: module reference, must be set by clocksource in modules
*
* Note: This struct is not used in hotpathes of the timekeeping code
* because the timekeeper caches the hot path fields in its own data
* structure, so no line cache alignment is required,
*
* The pointer to the clocksource itself is handed to the read
* callback. If you need extra information there you can wrap struct
* clocksource into your own struct. Depending on the amount of
* information you need you should consider to cache line align that
* structure.
*/
struct clocksource {
cycle_t (*read)(struct clocksource *cs);
cycle_t mask;
u32 mult;
u32 shift;
u64 max_idle_ns;
u32 maxadj;
struct arch_clocksource_data archdata;
u64 max_cycles;
const char *name;
struct list_head list;
int rating;
int (*enable)(struct clocksource *cs);
void (*disable)(struct clocksource *cs);
unsigned long flags;
void (*suspend)(struct clocksource *cs);
void (*resume)(struct clocksource *cs);
/* private: */
/* Watchdog related data, used by the framework */
struct list_head wd_list;
cycle_t cs_last;
cycle_t wd_last;
struct module *owner;
};
3.1. register/unregister clocksource
系统中使用cycle_t cycles 进行计数, 为了人们的方便会转换成年月日方式,所以就会用mult, shift(乘法,除法系数)进行转换。
1 | static inline s64 clocksource_cyc2ns(cycle_t cycles, u32 mult, u32 shift) |
1 | /* need to calculate mult, shift by caller */ |
3.2. OS选择clock source
主要参看的因素有两个:
- best rate (分辨率越高的)
- 用户空间的选择
1
static void __clocksource_select(bool skipcur)
3.3. timecounter 与 cyclecounter
具体来讲, cyclecounter 表示free running system counter 绝对的时间点, 而timecounter 表示counter, 但是表达的是ns 时间单位。
1 | /** |
4. clockevent
clockevent 数据结构如下
1 | /** |
上面重要的有1
2
3
4
5
6
7 /* set next event interrupt by cyclecounter or ktime */
int (*set_next_event)(unsigned long evt, struct clock_event_device *);
int (*set_next_ktime)(ktime_t expires, struct clock_event_device *);
/* switch event mode: periodic or oneshot */
int (*set_state_periodic)(struct clock_event_device *);
int (*set_state_oneshot)(struct clock_event_device *);
4.1. 常用函数
1 | extern void clockevents_config_and_register(struct clock_event_device *dev, |
在我们register clockevnet 后, 上层的tick layer 可能会考虑替换当前的clockevent device.
替换参考的依据是:
- 首先是CPU local device
- 具备更好的rate
如果current clockevent device 是broadcast device(broadcost clockevent device 主要用于在CPU sleep 时,其他CPU local timer 已经睡眠,在resume时我们可以通过broadcast device 唤醒其他CPU),需要先close.
1 | /* linux-4.9.198 code */ |