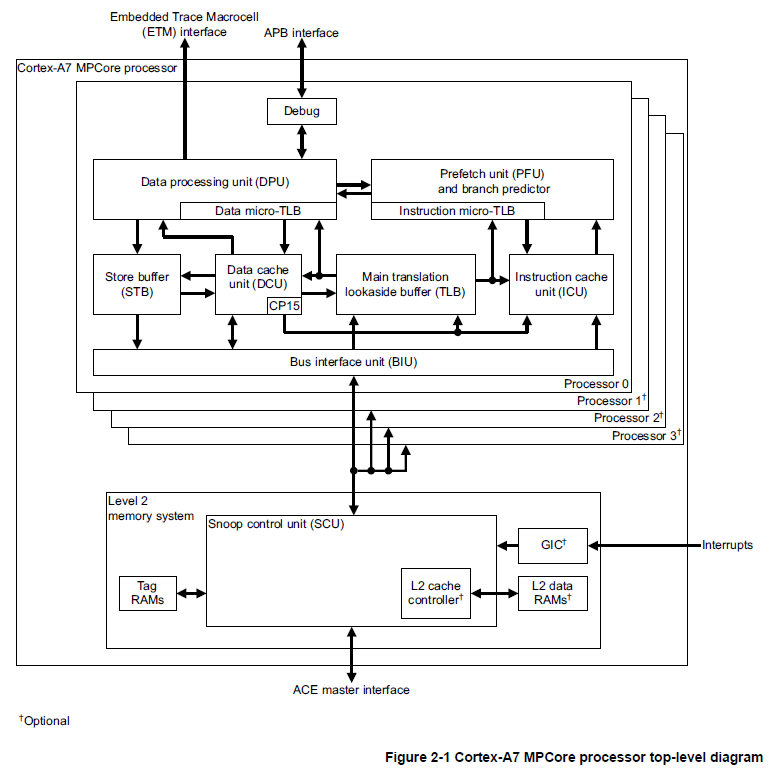
从ARM Cortex-a7 mpcore(armv7)的架构图上可以看出, cortex-a7 每个核独享各自L1 cache, 共享L2 cache(使用snoop control unit, soc 保证per core 数据的一致性)。
cache 分为:
- Data Cache
- Instruction Cache
1. Base
cache 对应与main memory 最小的unit 为cache line. 一个有效的cache 由两部组成:寻址 + 数据
cache = tag array + data array
example:
cache size 64 byte, cache line 8 byte.
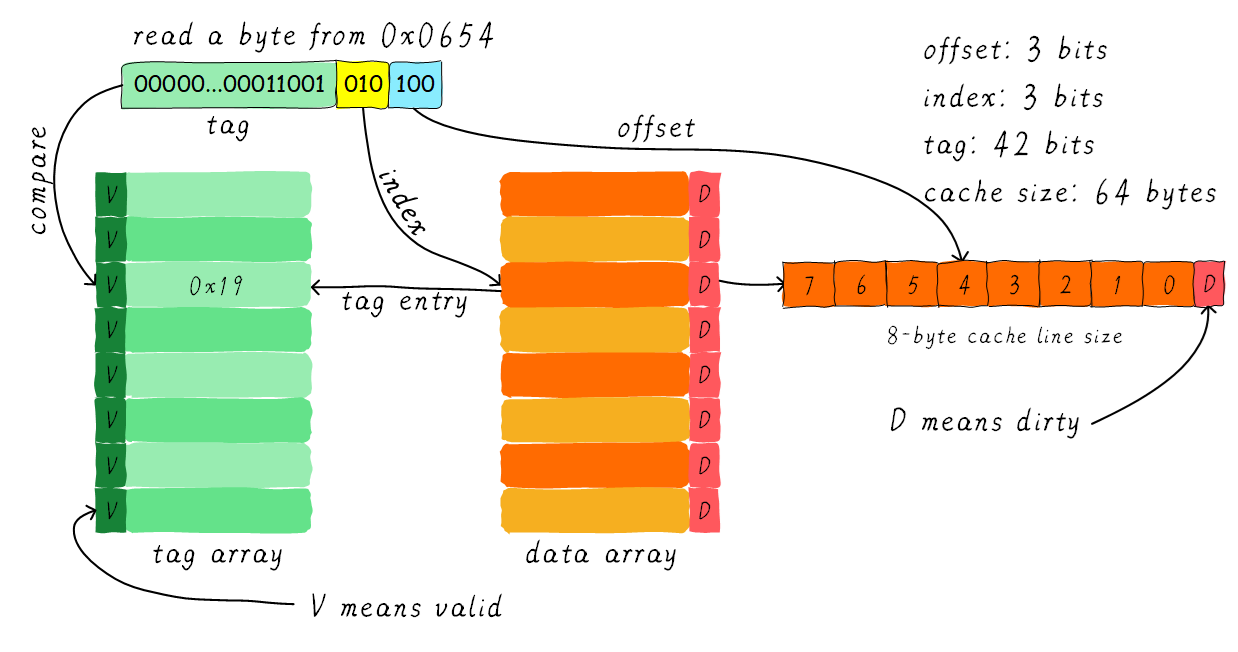
offset: 对应cache line 内中的偏移量
index: 指向which cache line
tag: 这个位宽除index, offset bits剩余部分

2. 映射方式
映射方式常有:
- 直接映射
- 组相连映射
- 全相连映射
2.1. 直接映射缓存(Direct mapped cache)
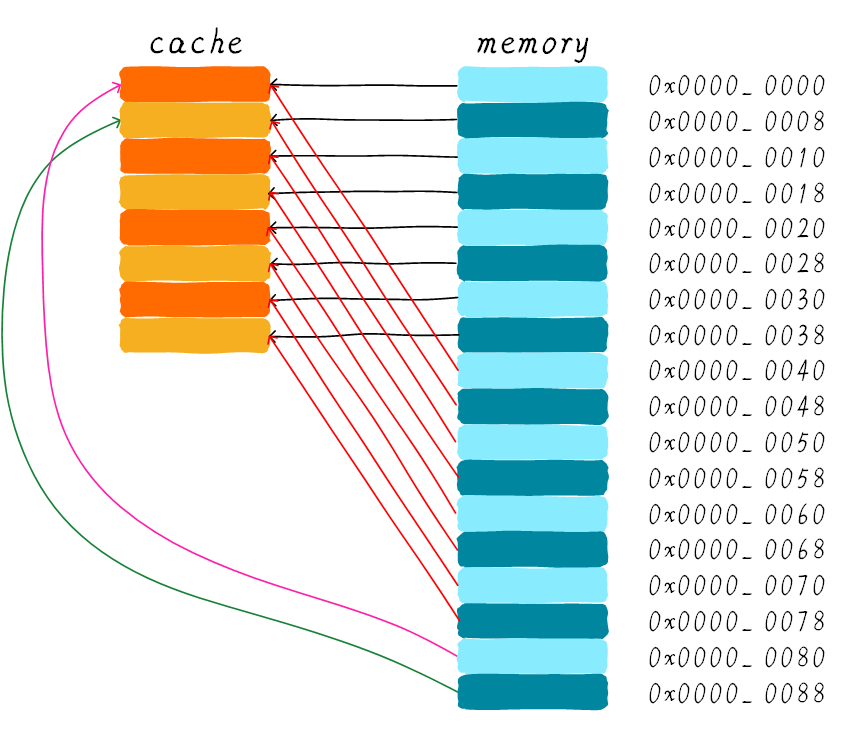
如果依次访问0x00, 0x40, 0x80 三者index 都相同,访问0x40 时, tag match失败,cache miss 重新加载数据,这种现象称为cache颠簸(cache thrashing)。 访问0x80, tag不同cache miss,重新加载数据。这种情况,cache的引入并没有性能有所提升,因此,引入了组相连映射。
2.2. 多路组相连缓存(multiple ways set associative cache)
平均将cache 分成多份,每一份就是一路(way)。在每一路中index 相同的cache lines称为组(set)。直接映射也可以称之为单路组相连。
多路组相连与直接映射对比:
| 优势 | 劣势 |
|---|---|
| 在相同的index 情况下, 如果一路(way) 中miss, 可以继续在另一路中寻找相同index 的cache line | 硬件成本更高,每次比较tag 需要比较多个cache line |
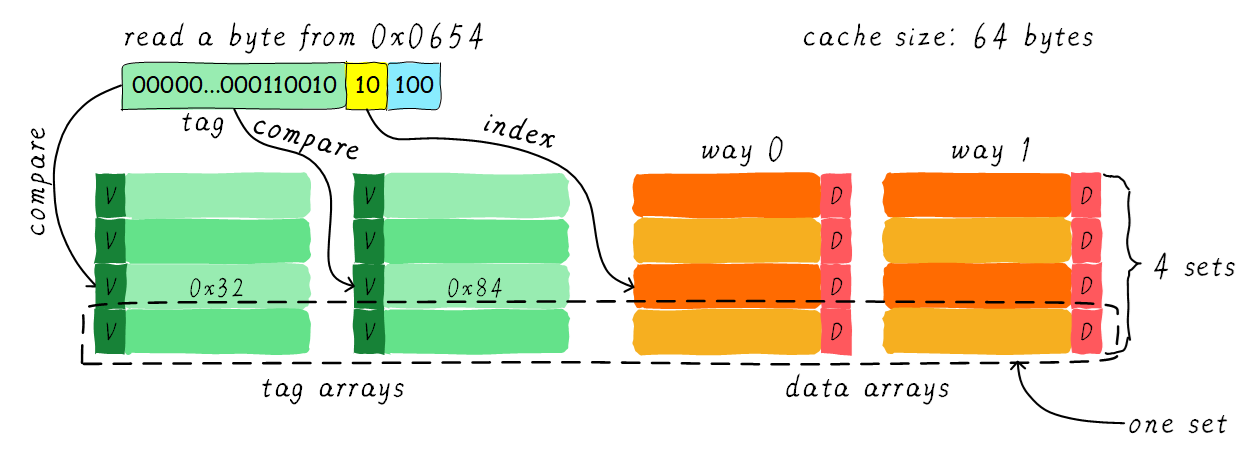
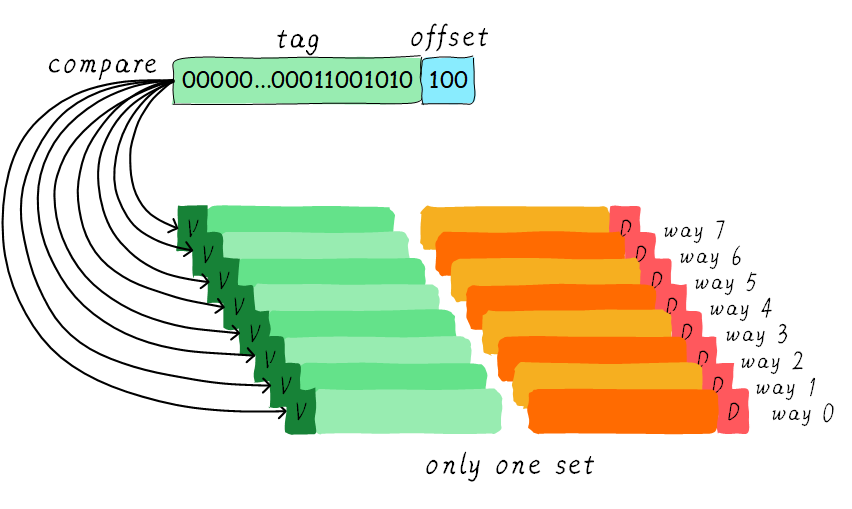
example: 32KB cache, 32 Bytes cache line, 4 ways, address bus 48-bit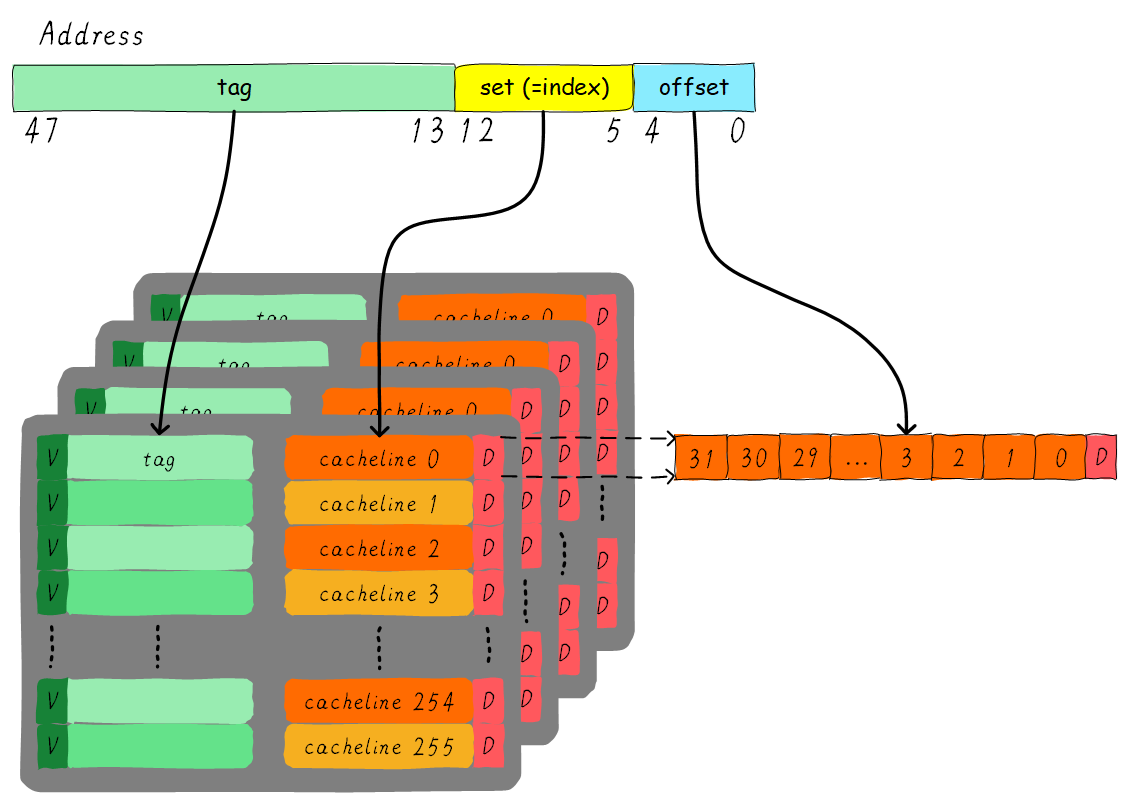
2.3. 全相连缓存(Full associative cache)
所有cache line 都在一个组内,因此,不需要index。任意地址的数据都可以缓存在任意cache line。但伴随硬件的成本,设计复杂度也会增加。
3. 更新策略
cache 更新策略是在cache 命中,并且有写操作时,cache 如何更新。
update policy 有两种:
- write through
- write back
3.1. 写直通(write through)
cache 更新的同时,main memory 也会一并更新。cache 与主存内容一致。
Fixme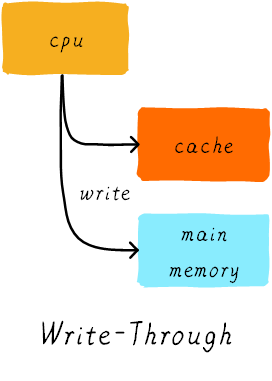
3.2. 写回(write back)
只更新cache, main memory 不更新。并且会置位 cache line中 “dirty bit”, 表明该cache line 修改过,并与主存不一致。在cache line 被替换时或flush 操作时更新到main memory。
Fixme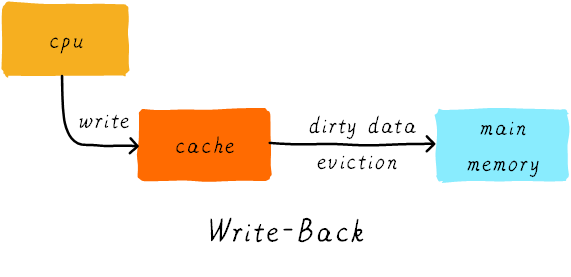
4. coherent
cache 的引入,Multiple Core, DMA 外设等因素,CPU Core访问的数据可能与另一个CPU Core或Device不一致。
4.1. memory attribute
比较直接的方式就是限制memory 的type 与attribute。例如设定成device type or strongly-ordered.
| type | shareablility | cacheability |
|---|---|---|
| strongly-ordered | outer shareable | Non-cacheable |
| device | outer shareable | Non-cacheable |
| normal | one of: - Non-shareable - inner shareable - outer shareable |
one of: - Non-cacheable - inner cacheable - outer cacheable |
4.2. cache 一致性协议
在cache line 增加状态位,表明当前cache line 的状态
MESI
| Status | Remarks |
|---|---|
| M 修改(modified) | cache line有效,数据被修改,与main memory 中不一致 |
| E 独享(Exclusive) | cache line 有效,数据与主存一致,并数据只存在于该cache line |
| S 共享(shared) | cache line 有效,数据与主存一致,数据存在于多个cache line |
| I 无效(invalide) | cache line 无效 |
状态图转换如下:
Fixme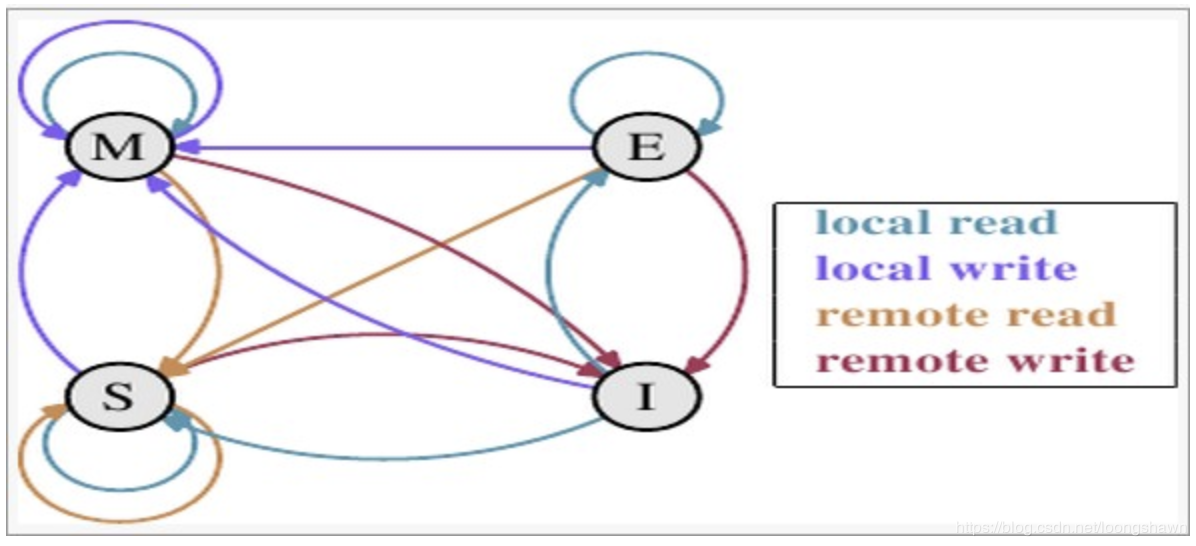
MOESI
相较于MESI,增加O(Owned), S也与MESI 定义不同,cache line 不一定与主存一致。M,E,I定义相同。
| Status | Remarks |
|---|---|
| M 修改(modified) | cache line有效,数据被修改,与main memory 中不一致 |
| O 拥有(Owned) | O为1, 当前cache line是当前cpu 最新数据拷贝,且其他core 一定具有该cache line 的副本状态位S |
| E 独享(Exclusive) | cache line 有效,数据与主存一致,并数据只存在于该cache line |
| S 共享(shared) | cache line 有效,数据与主存不一定一致,数据存在于多个cache line |
| I 无效(invalide) | cache line 无效 |
Fixme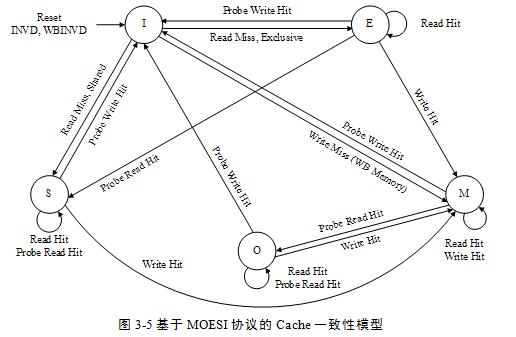
4.3. automic operating
ARM 提供了原子操作的指令,ldrex, strex, clrex系列指令。这能保证在多核之间对数据进行唯一性的访问。
配对使用的指令:
| load instruction | store instruction | remarks |
|---|---|---|
| ldrexb | strexb | byte access |
| ldrexh | strexh | half world access |
| ldrexd | strexd | double world access |
1 |
|
5. Cache Maintenance Operations
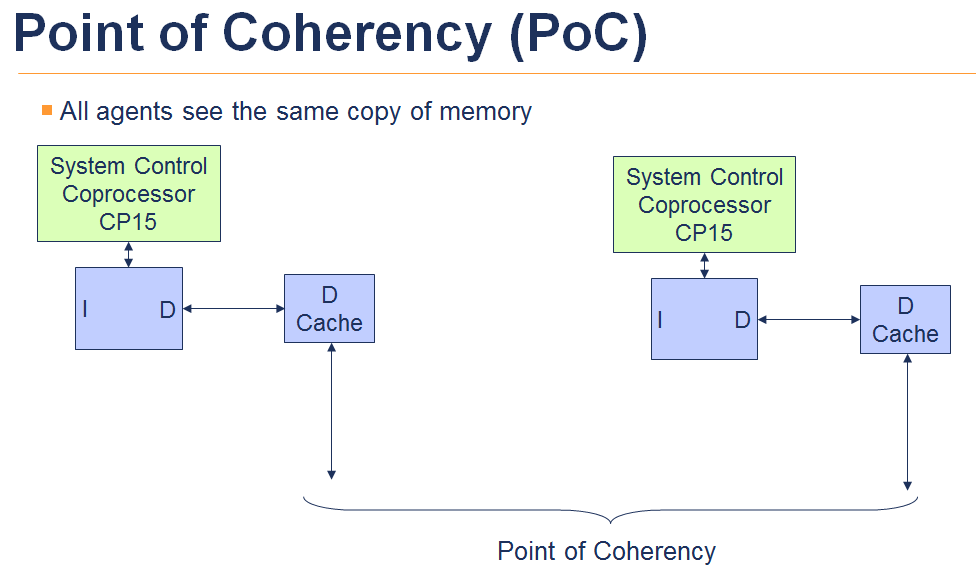
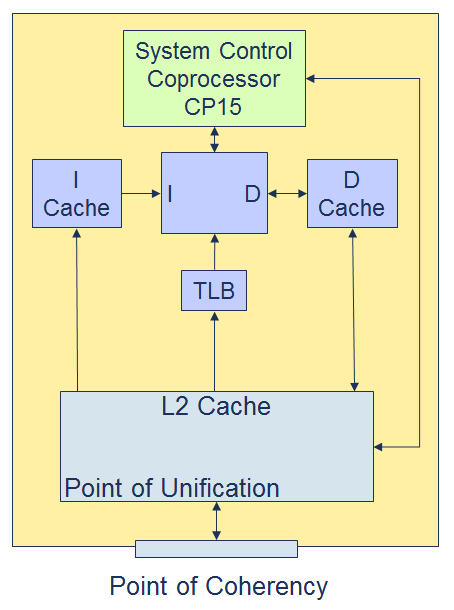
armv7 下cache 可以依据MVA(modified virtual address),set/way或全部内容进行维护更新,可参看如下图: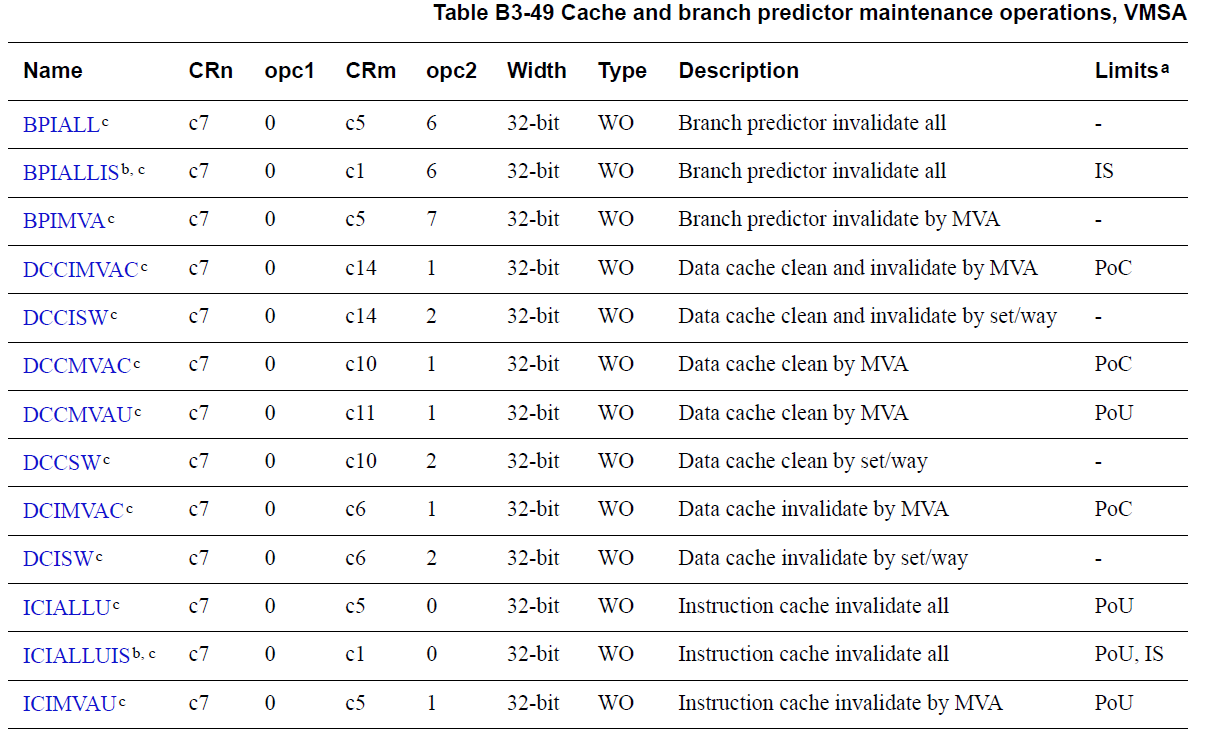
POU - to point of unification
POC - to point of coherence
POU 主要指Instruction, data, TLB 看到的为同一份mem
POC 主要指各个Core 之间看到的为同一份mem。
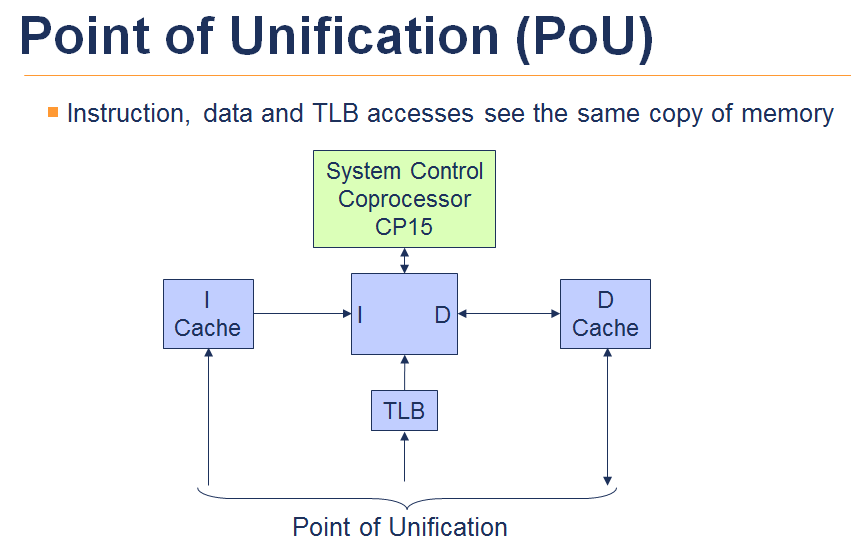
Reference
浅谈Cache Memory
缓存一致性协议MESI和MOESI
MESI & MOESI 协议
arm64 memory 属性 Device-nGnRnE
ARM平台下独占访问指令LDREX和STREX的原理与使用详解
什么是PoU和PoC?