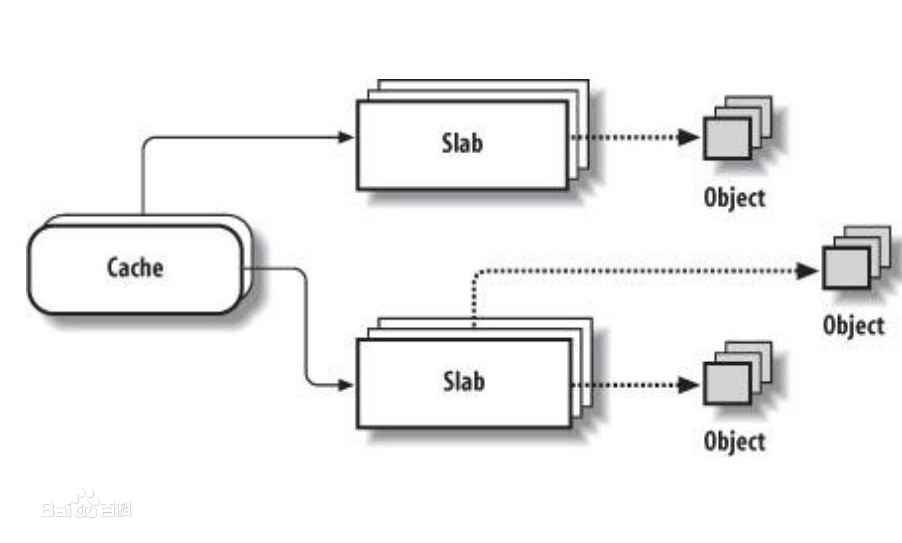
1. 前言
在linux mm 的分配主要有两种算法:伙伴算法(buddy system), slab alloctor。
| 伙伴算法 | slab 分配器 |
|---|---|
| 以页为单位进行管理分配 | 以字节为单位,8B, 16B, 32B, … 192B等 |
slab alloctor 从linux 的发展看已有三种分配策略:
- slab
- slub
- slob
Q: 为什么出现slab?
A: 伙伴算法管理粒度page 为单位, slab 的出现是为了管理小size 的内存
Q: 为什么出现slub, slob?
slab 管理数据复杂, 不支持NUMA(Non unified memory arcihtecture), 调试困难。
slub 对算法做了简化,针对SMP, NUMA系统优化,slub 对slab 的API 兼容。
slob 用于小size 的mm 上管理内存。
因此, 下面主要分析slub 分配算法。
2. data structure
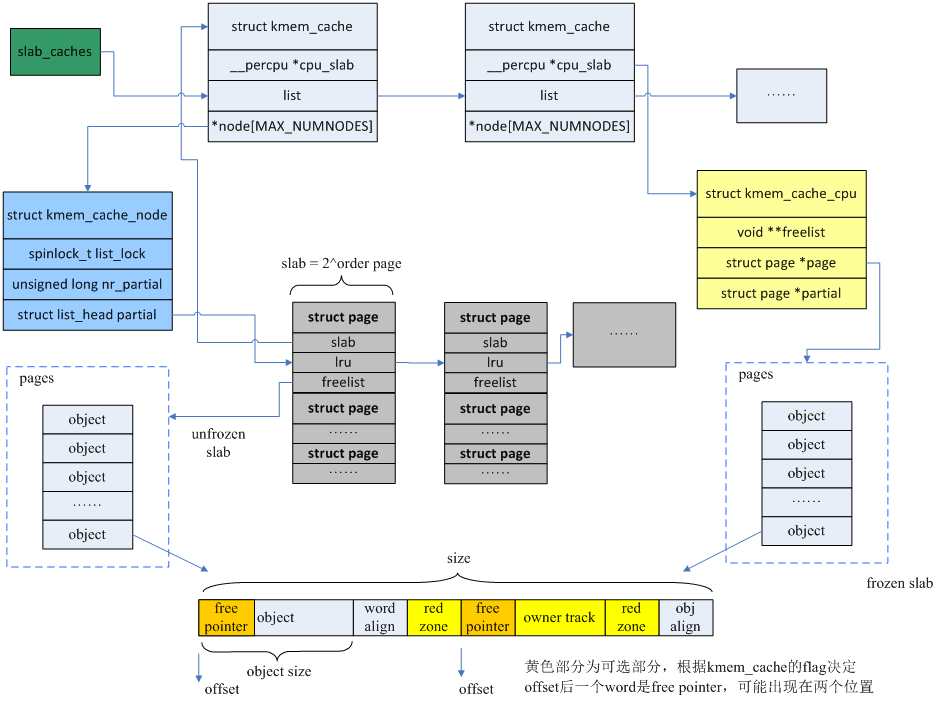
slab 相当于零售商,struct kmem_cache下有两个部门,仓库 struct kmem_cache_node, 营业厅struct kmem_cache_cpu。营业厅销售某种类型的object(如8 byte, 16 byte …, 具体的size 有零售商slab struct kmem_cache 决定), 我们可以从如下的kmem_cache_create() 函数看出strcut kmem_cache与size 的关系。
1 | struct kmem_cache *kmem_cache_create(const char *name, |
1 | /* Slab cache management. */ |
struct kmem_cache_cpu __percpu *cpu_slab 中限定__percpu 指明了是每一个CPU,可以理解为本地缓冲池。
struct kmem_cache_node *node[MAX_NUMNODES]; 是所有CPU 共享的, 而__percpu *cpu_slab 是每个CPU 独占的。
1 | struct kmem_cache_cpu { |
当从full object 上free 时,partial 将会指向此page。struct kmem_cache 中cpu_partial 将会限制 partial 的total 数目,过多的 * partial 将会回收到struct kemem_cache_node 仓库中。
1 | /* |
partial 指向仍有空闲object page, 当nr_partial 大于struct kmem_cache 中min_partial 时,完全free object 的page 将会伙伴系统回收。
3. work flow
slub把内存分组管理,每个组分别包含2^3、2^4、…2^11个字节,在4K页大小的默认情况下,另外还有两个特殊的组,分别是96B和192B,共11组。之所以这样分配是因为如果申请2^12B大小的内存,就可以使用伙伴系统提供的接口直接申请一个完整的页面即可。
3.1. allocate
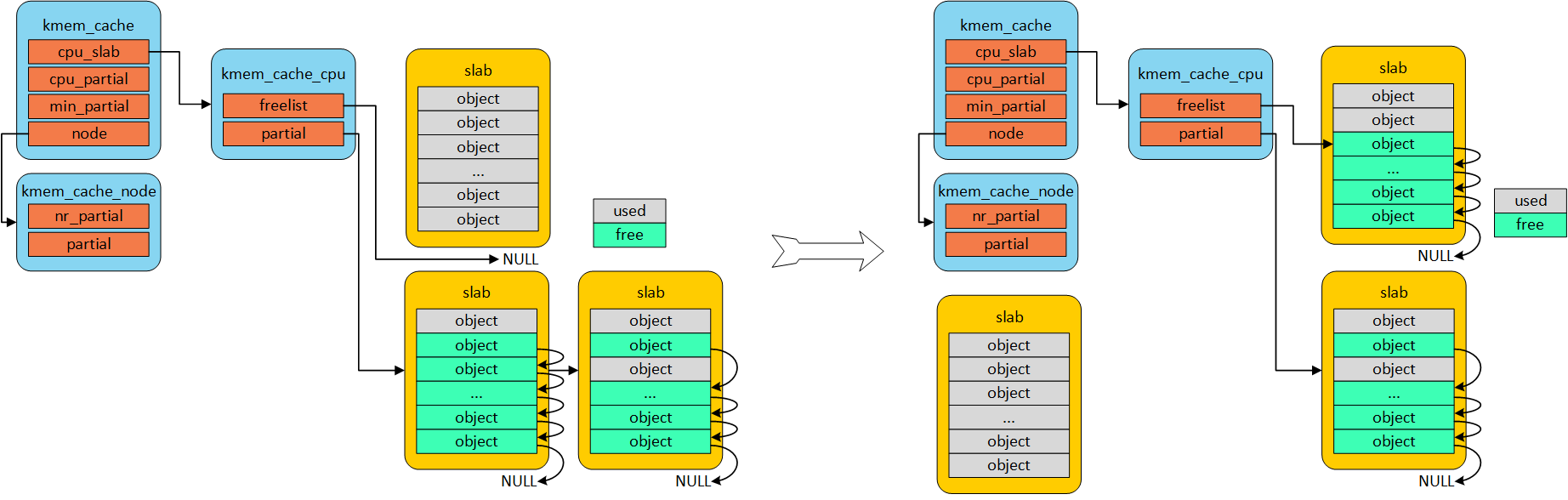
当内存申请的时候,优先从本地cpu缓存池申请。在分配初期,本地缓存池为空,自然从伙伴系统分配一定页数的内存。kmem_cacche_cpu中page就会指向正在使用的slab的页帧。freelist成员指向第一个可用内存object首地址。
kmem_cache 初始阶段,没有对象可分配时,从伙伴系统获取一个slab
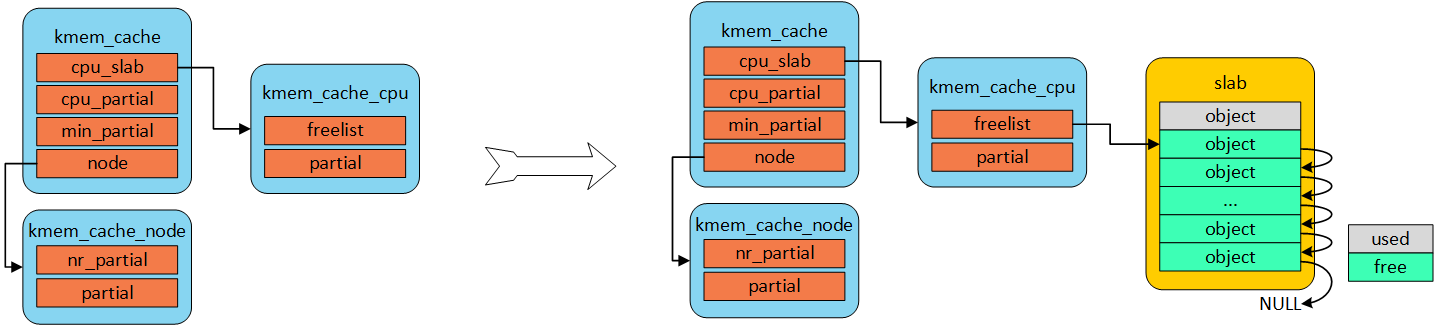
若kmem_cache_cpu 中无可用object时,尝试从kmem_cache_cpu 指向仍有可用object 的partial 获取
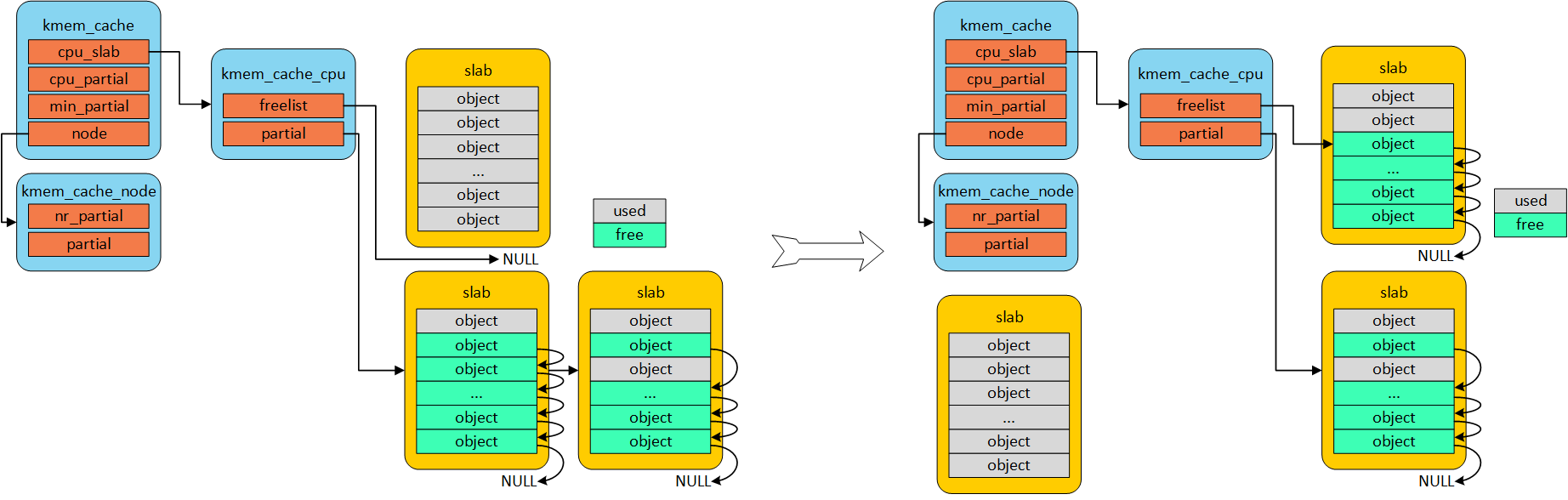
若kmem_cache_cpu 与 partial 中无可用object时,尝试从kmem_cache_node 获取
3.2. free
我们再free 时,free 的对象可能来自:
- full object page
- kmem_cache_cpu
- kmem_cache_cpu partial
- kmem_cache_node
总的原则是:kmem_cache_cpu 保有一定量的partial, kmem_cache_node 保有一定量partial
- free full 中object, 将kmem_cache_cpu partial 指向他
- 若kmem_cache_cpu partial 数目大于kmem_cache 中cpu_partial 时,将多的partial 放置到仓库kmem_cache_node
- 若kmem_cache_node partial 数目大于kmem_cache 中min_partial 时,则将free page 给budy system
free object in kmem_cache_cpu partial && kmem_cache_cpu && kmem_cache_node
直接标记该object 为free 状态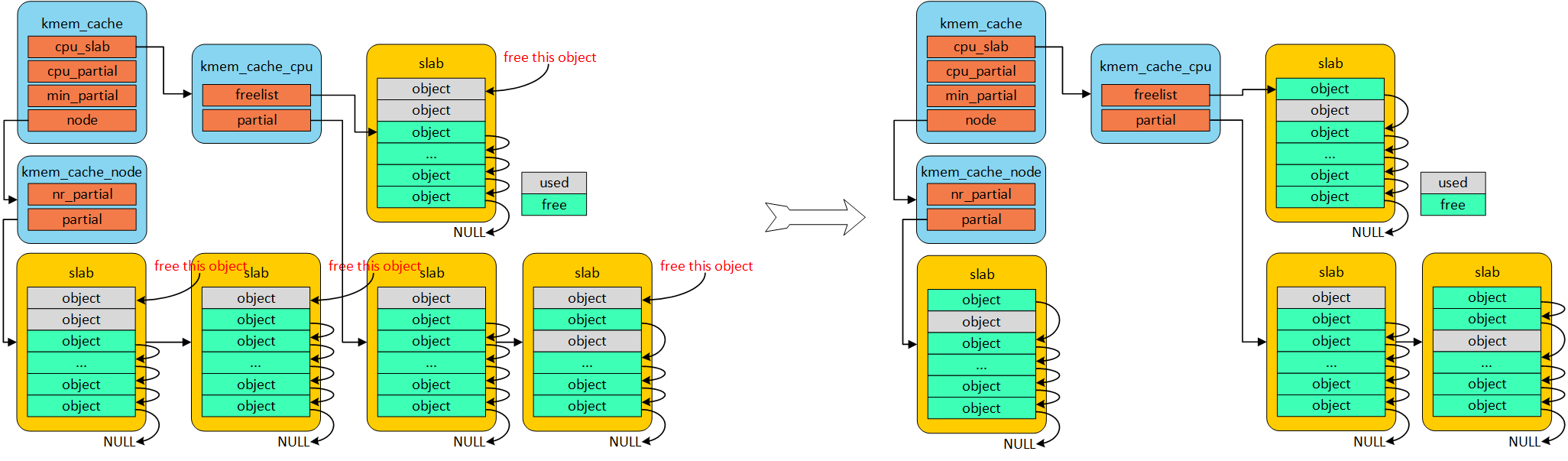
free object in full object page
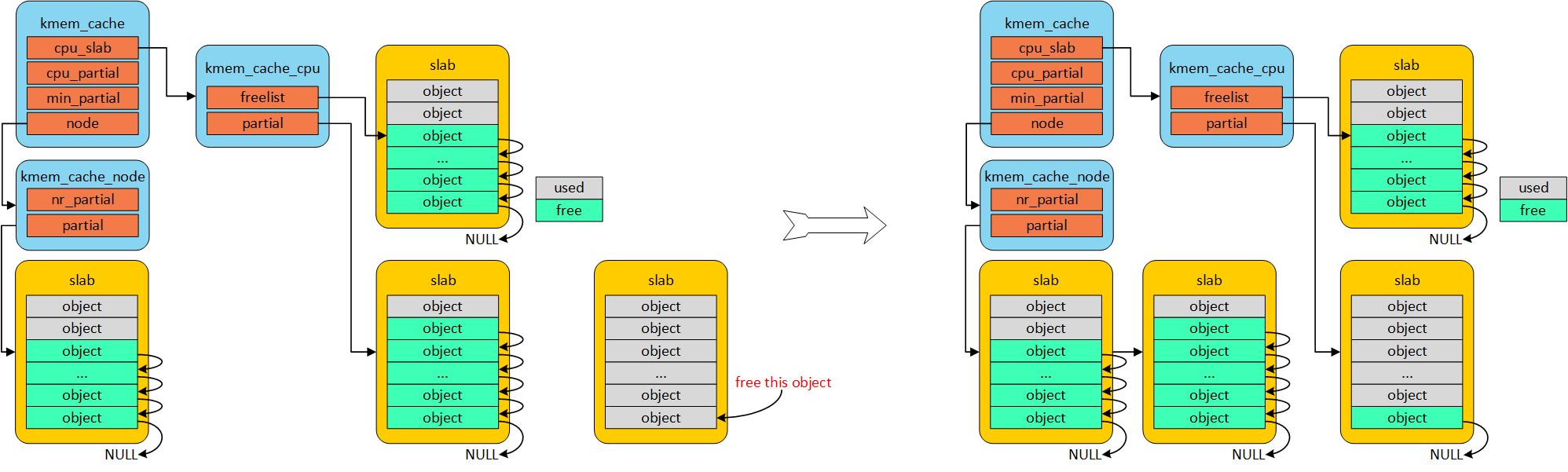
若kmem_cache_cpu partial 数目多于设定kmem_cache cpu_partial, 则将存储指仓库kmem_cache_node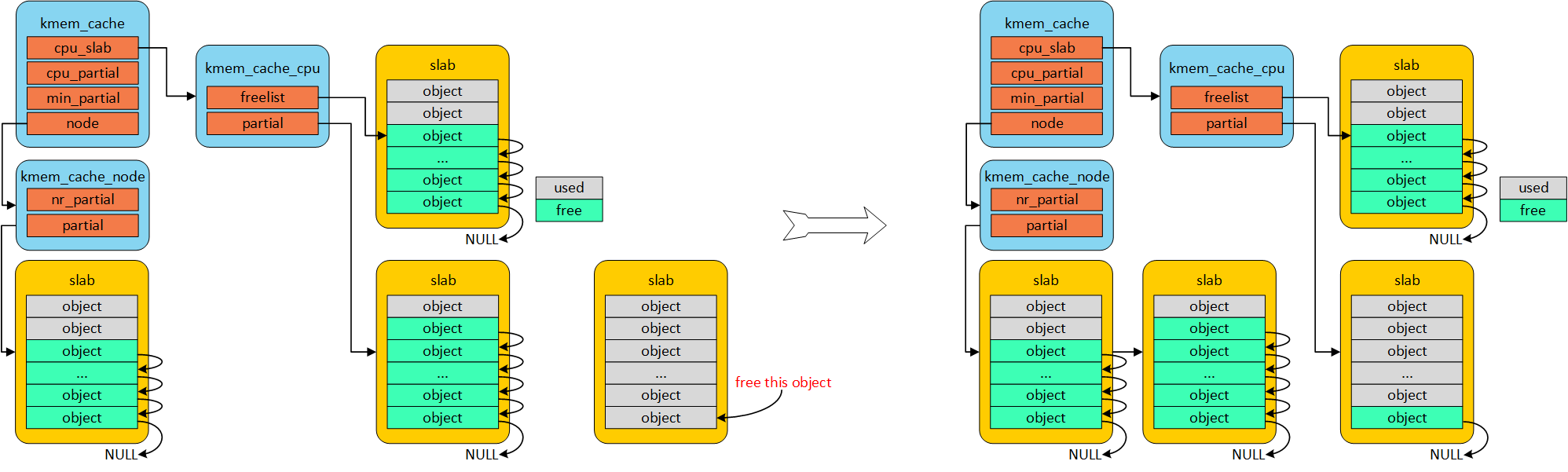
若仓库中堆满,kmem_cache_node partial 数目多于设定kmem_cache min_partial,则将规划至伙伴系统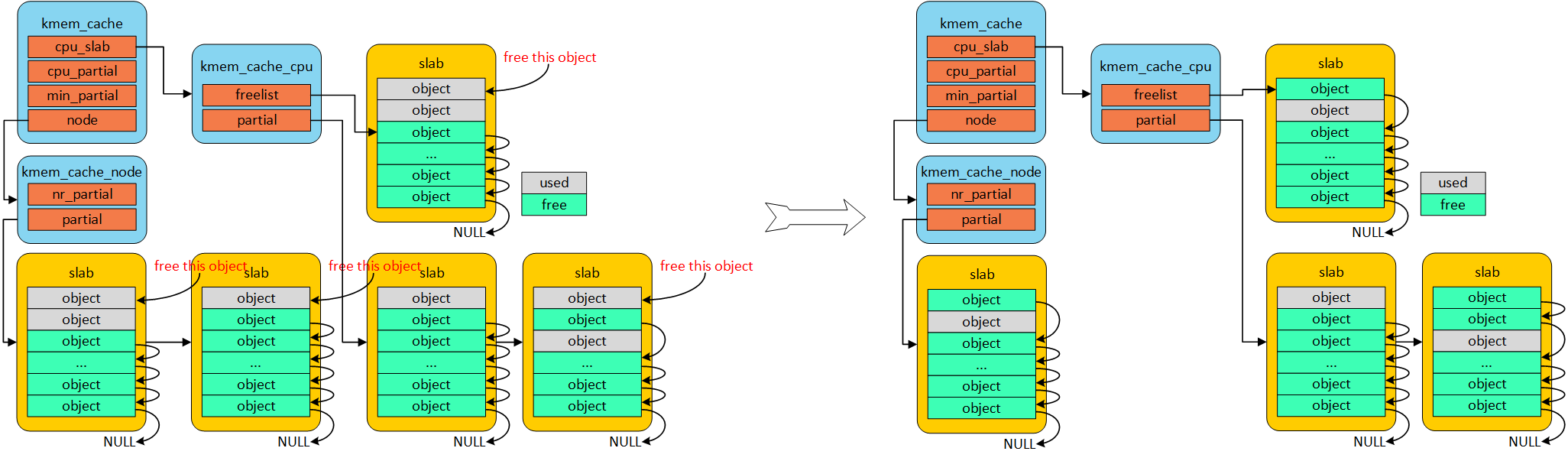
我们可以看看kmalloc 的实现, 其中返回kmalloc_caches[index], 那他是在哪里被初始化呢?
1 | struct kmem_cache *kmalloc_caches[KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH + 1]; |
在slub.c1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58/** linux/mm/slub.c*/
void __init kmem_cache_init(void)
{
...
create_kmalloc_caches(0);
}
void __init create_kmalloc_caches(unsigned long flags)
{
int i;
for (i = KMALLOC_SHIFT_LOW; i <= KMALLOC_SHIFT_HIGH; i++) {
if (!kmalloc_caches[i])
new_kmalloc_cache(i, flags);
/*
* Caches that are not of the two-to-the-power-of size.
* These have to be created immediately after the
* earlier power of two caches
*/
if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 32 && !kmalloc_caches[1] && i == 6)
new_kmalloc_cache(1, flags);
if (KMALLOC_MIN_SIZE <= 64 && !kmalloc_caches[2] && i == 7)
new_kmalloc_cache(2, flags);
}
/* Kmalloc array is now usable */
slab_state = UP;
}
/*
* kmalloc_info[] is to make slub_debug=,kmalloc-xx option work at boot time.
* kmalloc_index() supports up to 2^26=64MB, so the final entry of the table is
* kmalloc-67108864.
*/
static struct {
const char *name;
unsigned long size;
} const kmalloc_info[] __initconst = {
{NULL, 0}, {"kmalloc-96", 96},
{"kmalloc-192", 192}, {"kmalloc-8", 8},
{"kmalloc-16", 16}, {"kmalloc-32", 32},
{"kmalloc-64", 64}, {"kmalloc-128", 128},
{"kmalloc-256", 256}, {"kmalloc-512", 512},
{"kmalloc-1024", 1024}, {"kmalloc-2048", 2048},
{"kmalloc-4096", 4096}, {"kmalloc-8192", 8192},
{"kmalloc-16384", 16384}, {"kmalloc-32768", 32768},
{"kmalloc-65536", 65536}, {"kmalloc-131072", 131072},
{"kmalloc-262144", 262144}, {"kmalloc-524288", 524288},
{"kmalloc-1048576", 1048576}, {"kmalloc-2097152", 2097152},
{"kmalloc-4194304", 4194304}, {"kmalloc-8388608", 8388608},
{"kmalloc-16777216", 16777216}, {"kmalloc-33554432", 33554432},
{"kmalloc-67108864", 67108864}
};
static void __init new_kmalloc_cache(int idx, unsigned long flags)
{
kmalloc_caches[idx] = create_kmalloc_cache(kmalloc_info[idx].name,
kmalloc_info[idx].size, flags);
}
后面的create_kmalloc_cache(),则是尝试找到freelist, 例如从kmem_cache_cpu freelist, partial获取object, 若都为空则使用new_slab()->alloc_slab_page()->alloc_pages() 分配page 生成free objects。
4. 调试手段
4.1. SLUB_DEBUG
SLUB DEBUG检测oob(out-of-bounds)问题原理:在分配出去的内存尾部添加额外空间–red zone, 并填充MAGIC,之后检测其内容。
SLUB DEBUG 检测uaf(use-after-free)问题原理:free 后,将object 数据填充MAGIC NUM(0X6B)
slub 管理的object 对象的格式如下: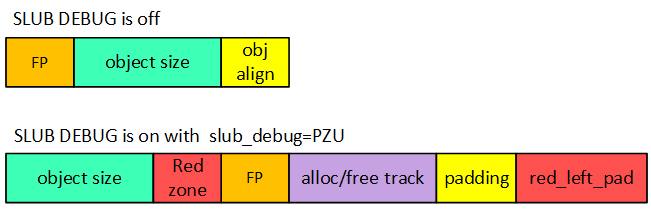
free pointer是从object后移就是因为为了检测use-after-free问题,当free object时会在将object填充magic num(0x6b)。
red zone
可以检测向后的越界访问
red left pad
可以检测向前的越界访问
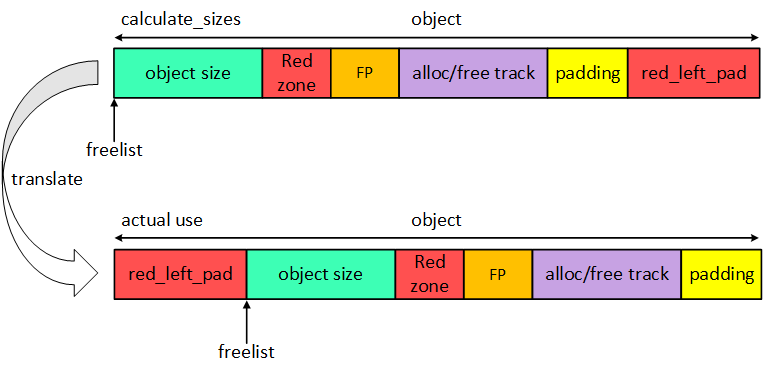
padding
填充填充magic num,可以检测较大空间的overwritten
Magic number1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9//linux/include/linux/poison.h
/* ...and for poisoning */
在slub alloc 一个object,经过init_object 填充magic num 后,会如下所示: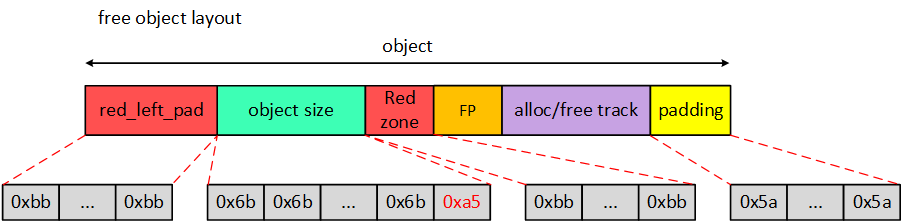
- red_left_pad和Red zone填充了SLUB_RED_INACTIVE(0xbb);
- object填充了POISON_FREE(0x6b),但是最后一个byte填充POISON_END(0xa5);
- padding在allocate_slab的时候就已经被填充POISON_INUSE(0x5a)
如果是oob(out-of-bounds),这red zone/red left pad magic num 会被修改,在kfree 时检测red zone/red left pad, 反之是uaf(use-after-free)时, 我们再free 后将object 填充为POISON_FREE(0x6b) + POISON_END(0xa5), 之后使用slabinfo 工具进行遍历检测free list mem,object 区域是否有被修改过。
4.2. KASAN
KASAN (kernel address sanitizer) runtime memory debugger, 是一个动态检测工具。Kernel doc 可参见Documentation/dev-tool/kasan.rst 文档。
我们从kernel menuconfig 中help 信息可以看出:
- GCC 4.9.2以上版本才支持debug 功能
- GCC 5.0以上版本支持栈、全局变量的越界访问
- 消耗1/8 内存用于跟踪记录
designed to find out-of-bounds accesses and use-after-free bugs.
This is strictly a debugging feature and it requires a gcc version
of 4.9.2 or later. Detection of out of bounds accesses to stack or
global variables requires gcc 5.0 or later.
This feature consumes about 1/8 of available memory and brings about
~x3 performance slowdown.
原理
KASAN 利用额外的内存(shadow memory, 影子区)标记内存状态,使用magic num 填充shadow memory,每一次R/w mem时都会检测shadow memory 是否valid。每连续8 bytes 使用1 byte shadow memory 标记。
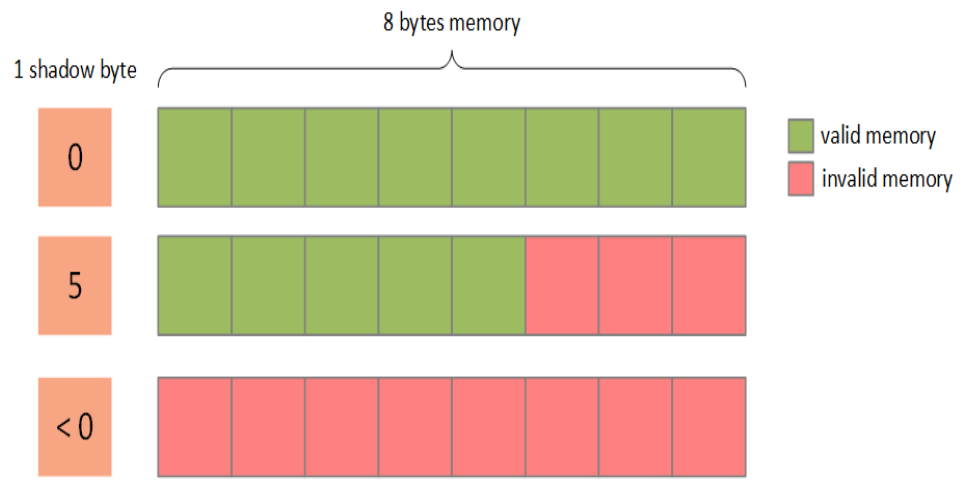
1 |
|
在高版本的gcc 中编译器编译时在mm access 插入asan_load/asan_store 函数。
arm64, VA_BITS=48, kernel 的mem layout. (KERNEL是不是位于linear mapping区域,这里怎么变成了VMALLOC区域?这里是Ard Biesheuvel提交的修改。主要是为了迎接ARM64世界的KASLR(which allows the kernel image to be located anywhere in the vmalloc area)的到来。)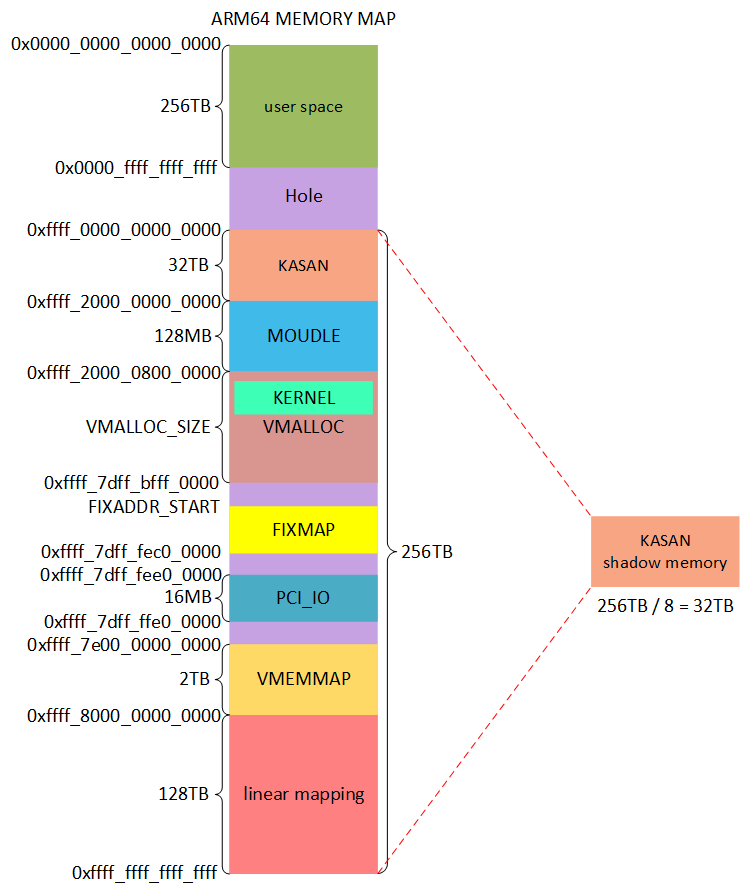
shadow_addr = (kaddr >> 3) + KASAN_SHADOW_OFFSE,在kasan_init()之后KASAN 就能正常工作,kernel 与 linear mapping 区域建立与shadow memory映射。若是module,则在load 时建立映射关系。
检测
大致与SLUB_DEBUG相同,通过填充KASAN_FREE_PAGE/KASAN_KMALLOC_FREE 来检测UAF(use-after-free), 填充KASAN_KMALLOC_REDZONE 到red zone检测OOB(out-of-bounds), 这针对于伙伴算法与slub allocator。在debug stack或global 变量时则需要GCC 编译器插入red zone。组成类似结构体:1
2
3
4struct {
type data;
char redzone;
}
结果
参见kernel 中Documentation/dev-tool/kasan.rst1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72==================================================================
BUG: AddressSanitizer: out of bounds access in kmalloc_oob_right+0x65/0x75 [test_kasan] at addr ffff8800693bc5d3
Write of size 1 by task modprobe/1689
=============================================================================
BUG kmalloc-128 (Not tainted): kasan error
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------
Disabling lock debugging due to kernel taint
INFO: Allocated in kmalloc_oob_right+0x3d/0x75 [test_kasan] age=0 cpu=0 pid=1689
__slab_alloc+0x4b4/0x4f0
kmem_cache_alloc_trace+0x10b/0x190
kmalloc_oob_right+0x3d/0x75 [test_kasan]
init_module+0x9/0x47 [test_kasan]
do_one_initcall+0x99/0x200
load_module+0x2cb3/0x3b20
SyS_finit_module+0x76/0x80
system_call_fastpath+0x12/0x17
INFO: Slab 0xffffea0001a4ef00 objects=17 used=7 fp=0xffff8800693bd728 flags=0x100000000004080
INFO: Object 0xffff8800693bc558 @offset=1368 fp=0xffff8800693bc720
Bytes b4 ffff8800693bc548: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 5a 5a 5a 5a 5a 5a 5a 5a ........ZZZZZZZZ
Object ffff8800693bc558: 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b kkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk
Object ffff8800693bc568: 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b kkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk
Object ffff8800693bc578: 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b kkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk
Object ffff8800693bc588: 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b kkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk
Object ffff8800693bc598: 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b kkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk
Object ffff8800693bc5a8: 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b kkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk
Object ffff8800693bc5b8: 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b kkkkkkkkkkkkkkkk
Object ffff8800693bc5c8: 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b 6b a5 kkkkkkkkkkkkkkk.
Redzone ffff8800693bc5d8: cc cc cc cc cc cc cc cc ........
Padding ffff8800693bc718: 5a 5a 5a 5a 5a 5a 5a 5a ZZZZZZZZ
CPU: 0 PID: 1689 Comm: modprobe Tainted: G B 3.18.0-rc1-mm1+ #98
Hardware name: QEMU Standard PC (i440FX + PIIX, 1996), BIOS rel-1.7.5-0-ge51488c-20140602_164612-nilsson.home.kraxel.org 04/01/2014
ffff8800693bc000 0000000000000000 ffff8800693bc558 ffff88006923bb78
ffffffff81cc68ae 00000000000000f3 ffff88006d407600 ffff88006923bba8
ffffffff811fd848 ffff88006d407600 ffffea0001a4ef00 ffff8800693bc558
Call Trace:
[<ffffffff81cc68ae>] dump_stack+0x46/0x58
[<ffffffff811fd848>] print_trailer+0xf8/0x160
[<ffffffffa00026a7>] ? kmem_cache_oob+0xc3/0xc3 [test_kasan]
[<ffffffff811ff0f5>] object_err+0x35/0x40
[<ffffffffa0002065>] ? kmalloc_oob_right+0x65/0x75 [test_kasan]
[<ffffffff8120b9fa>] kasan_report_error+0x38a/0x3f0
[<ffffffff8120a79f>] ? kasan_poison_shadow+0x2f/0x40
[<ffffffff8120b344>] ? kasan_unpoison_shadow+0x14/0x40
[<ffffffff8120a79f>] ? kasan_poison_shadow+0x2f/0x40
[<ffffffffa00026a7>] ? kmem_cache_oob+0xc3/0xc3 [test_kasan]
[<ffffffff8120a995>] __asan_store1+0x75/0xb0
[<ffffffffa0002601>] ? kmem_cache_oob+0x1d/0xc3 [test_kasan]
[<ffffffffa0002065>] ? kmalloc_oob_right+0x65/0x75 [test_kasan]
[<ffffffffa0002065>] kmalloc_oob_right+0x65/0x75 [test_kasan]
[<ffffffffa00026b0>] init_module+0x9/0x47 [test_kasan]
[<ffffffff810002d9>] do_one_initcall+0x99/0x200
[<ffffffff811e4e5c>] ? __vunmap+0xec/0x160
[<ffffffff81114f63>] load_module+0x2cb3/0x3b20
[<ffffffff8110fd70>] ? m_show+0x240/0x240
[<ffffffff81115f06>] SyS_finit_module+0x76/0x80
[<ffffffff81cd3129>] system_call_fastpath+0x12/0x17
Memory state around the buggy address:
ffff8800693bc300: fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc
ffff8800693bc380: fc fc 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 fc
ffff8800693bc400: fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc
ffff8800693bc480: fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc
ffff8800693bc500: fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc 00 00 00 00 00
>ffff8800693bc580: 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 03 fc fc fc fc fc
^
ffff8800693bc600: fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc
ffff8800693bc680: fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc fc
ffff8800693bc700: fc fc fc fc fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb
ffff8800693bc780: fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb
ffff8800693bc800: fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb fb
==================================================================